This is a very interesting report, which was written by my friend Kay the Guru. It deals with the breeding of Dynastes hercules hercules.
1. Introduction
Hello Friends! My name is Kay and I am a beetle breeding/rearing hobbyist from Japan.
First of all, I would like to tell you about a brief history of a rather new fad, beetle breeding/rearing, in my country. Year 1986 became a milestone for the beetle business in Japan. That year, Hiroshi Kojima, an acquaintance of mine, introduced an article on his success in the breeding of Dorcus hopei binodulosus, the then most popular stag beetle that were sold at rather high prices. By then, because of their high commercial values, they had been over collected here, thus became rather rare in nature. And yet, much of their life cycle had been veiled with mysteries. Kojima’s article shed a light on their life cycle and their breeding/rearing. Within a short time, a variety of beetle breeding/rearing articles (substrates, foods, containers, etc.) were developed for the purpose of mass-reproducing the beetles. Soon, the species were reproduced in a large quantity and the new pet business – beetle breeding/rearing – had begun. Moreover, in 1999, ninety-nine living exotic beetle species became importable to Japan which include Dynastes, Megasoma, Chalcosoma, etc. And more species had been added to the import list from time to time. Over the course of time, some of the species had been reared to a point where they exceed the maximum length that they attain in nature. It is said that there are about 3 million beetle hobbyists in Japan. Now, living beetles from around the world are readily available at supermarkets and pet shops throughout the country. There are even ‘beetle’ shops here.
My particular concerns are the breeding/rearing of giant beetles, the maximum length of whose males exceeds 100 mm in nature (See the following list: Giant Rhinoceros Beetles). Among them, Dynastes hercules hercules is my most favorite
Giant Rhinoceros Beetles:
1) Dynastes hercules (hercules of Guadeloupe: max. 180 mm?);
2) Dynastes neptunus (max. 158 mm);
3) Megasoma mars (max. 140 mm?);
4) Megasoma elephas (elephas: max. 136 mm?);
5) Megasoma actaeon (max. 135 mm?);
6) Chalcosoma chiron (janssensi of Sumatra Is.: max. 133 mm);
7) Megasoma janus (janus: max. 120 mm);
8) Megasoma gyas (gyas of Brazil: max. 116 mm);
9) Dynastes satanas (Bolivia: max. 115 mm);
10) Megasoma occidentalis (Mexico: max. 112 mm);
11) Chalcosoma moellenkampi (Kalimantan Is.: max. 112 mm); and
12) Chalcosoma atlas (hesperus of Mindanao Is.: max. 108 mm)
The following pages present the breeding/rearing of Dynastes hercules hercules. Discussion on the breeding/rearing follows natural history of the insect, which is thought useful for breeding/rearing. Although the classification of the species may vary among taxonomists, there are 13 varieties (S. Nagai):
1) hercules Linneaeus, 1758
(max. 180mm?; Guadeloupe and Dominica);
2) ecuatorianus Ohaus, 1913
(max. 165 mm; Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Brazil and Bolivia);
3) baudrii Pinchon, 1976
(max. 100 mm; Martinique);
4) reidi Chalmeau, 1977
(max. 105 mm; St. Lucia);
5) lichyi Lachaume, 1985
(max. 172 mm; Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru and Bolivia);
6) occidentalis Lachaum, 1985
(max. 145 mm; Panama, Colombia and Ecuador);
7) septentrionalis Lachaume, 1985
(max. 140 mm; Central America);
8) paschoali Grossi et Arnaud, 1993
(max. 145 mm; Brazil);
9) tuxtlaensis Moro’n, 1993
(max. 110 mm; Mexico);
10) bleuzeni Silvestre et Dechambre, 1995
(max. 151 mm; Venezuela);
11) trinidadensis Chalumeau et Reid, 1995
(max. 137 mm; Trinidad and Tobago);
12) morishimai Nagai, 2002
(max. 120 mm; Bolivia); and
13) takakuwai Nagai, 2002
(max. 130 mm; Brazil)
Ssp. hercules is considered as the longest living rhinoceros beetle in the world. A number of sources say that 180 mm may be the maximum length of a wild-caught male imago of Guadeloupe. That means, for beetle breeding/rearing enthusiasts, that the male of this subspecies has a potential of growing up to 180 mm long or even longer. Note that, owing to the collaboration of breeders and hobbyists, some substrates for breeding/rearing Dynastinae were developed and hence, by using them, some breeders/rearers in Japan, both professionals and hobbyists, have reported the rearing of males of this variety from eggs to imagoes of over 150-160 mm in length (brief description of a substrate is presented in 4. A breeding/rearing substrate). The following discussion limits ssp. hercules, first introducing its natural history and then emphasizing its breeding/rearing method to win good results. However, this breeding/rearing method can be applied to many other Dynastinae.
2. Natural history
2.1 Description: Male 46-180? mm including horns; Female 50-80 mm. Dull black on prothorax and yellowish-brown on fore wings. Male’s horns have several small teeth along inner edge, and are slightly bent inwardly at tip. Head of a large male reaches to the length of its prothorax and abdomen combined.
2.2 Habitat: Tropical rain forests.
2.3 Range: Ssp. hercules is confined to Guadeloupe and Dominica.
2.4 Food: Imago saps tree juice and larva seems to feed rotten hardwood tree.
2.5 Life cycle: The insect life is said to be largely unknown in a natural setting. Under captive rearing (26 degrees C. in summer; 18 degrees C. in winter) using an artificial substrate, however, the author has experienced the following:
Upon the transfer of larvae singly into rearing containers filled with substrate,
1. Duration of larva:
Male: 12-18 months (L1: 1 month; L2: 2 months; and L3: 9-15 months); and
Female: 12 months (L1: 1 month; L2: 2 months; and L3: 9 months)
2. alias of pupa: 2-3 months
Note that the duration of egg is said to be about 1 month.
3. Breeding/rearing
3.1 Getting started
To begin with, what you need are:
1) An imago pair (or several larvae);
2) Containers for breeding/rearing;
3) Food for imagoes; and
4) Substrate for breeding/rearing
1) If you live in a country where this beetle is sold, please obtain an imago pair (or several larvae). In choosing which individuals to buy, the following criteria are useful:
a) Wild-caught individuals:
Make sure: – When were they collected?: Avoid older individuals.
– Are they healthy-looking?: Check if there is no scar, injury
or missing part.
b) Captive reared individuals:
Make sure: – When did they emerge?: Avoid individuals of 8 months or older.
– Are they healthy-looking?: Check if there is no scar, injury
or missing part.
* Note that these two criteria are for imagoes. For choosing larvae, you can skip steps: – When were
they collected? and – When did they emerge?
2) Oviposition (egg laying) requires some space; e.g. a large container with a capacity of 45-60 liters (an example is a fish tank and a lid is a must to stop the beetles from escaping). Get one and fill it with substrate (see 4. A breeding/rearing substrate).
– Put substrate into the container up to 20 cm high from the bottom, and press it hard by hand or any other means. Then, another 10 cm depth of substrate should be added softly to the top of the layer. Often times, female concerns depth and lays eggs in the hard-pressed bottom layer.
– It would be better to place several small tree branches or wood sticks on the surface of the substrate. By holding them, beetles can easily get up in case turning upside down on their back.
– Then, let a pair of beetles into the container. Feed them regularly (for food, see 3)).
– Keep temperature at 20-26 degrees C. and moisten the substrate adequately.
3) For maintaining imagoes, you need to feed them with a pealed banana. It is better to place its pieces or slices on a small tray instead of applying them directly on the substrate, which causes them spoiling faster or prompts an occurrence of fruit flies or ticks. I hear that a pealed apple or a peach also serves as a suitable food.
4) See 4. A breeding/rearing substrate.
3.2 Rearing larvae
One or two months after you let the imago pair into the breeding container, look into the substrate if larvae have already hatched. If so, take the imagoes out of the container, and keep the larvae in the container until they become second-instar (L2)*. To win better results of larval growth, keep males separated from females at L2 stage and transfer the males singly into a large rearing container, preferably of a 45-60 liter capacity. However, if you do not expect males to grow to the maximum, you can rear them together in a fairly large container or put them singly into a container of a smaller capacity (e.g. 5-6 liters). For females, you can rear them together in a large container. But, the less in number, the larger they seem to grow. But again, if you also expect females to grow to the maximum, you should put them singly into a container of 5-6 liters in capacity.
* If you wish to obtain more eggs, let the imago pair into another breeding container. Repeat this
process if you want.
You need to change substrates from time to time. You can put gardening black dirt up to 15 cm high from the bottom of the container, and press it hard. The black dirt layer makes larvae easier to make a pupal cell in their last larval stage. Note that black dirt is NOT food and you do not have to remove it each time you change rearing substrates. For male larvae, I change rearing substrates of a 60 liter container every 6 months over the course of a larval period of about one and a half year or until larvae turn noticeably yellowish in colour. However, if you use a smaller container for rearing a male larva, you need to change substrates more often. A reliable sign for a change is larva’s dung. If it becomes noticeable, then you change substrates. When changing substrates, it is safer to lay unused (new) substrate first, and then used one. Do not press rearing substrate hard in order to keep it well-ventilated. The capacity ratio of the new to the used is 2-to-1. By so doing, beetle’s symbiotic bacteria, if any, would grow steadily in the substrate and enhance an ideal feeding environment for better larval growth (H. Kojima). For females, you can change rearing substrates when dung appears noticeable in the substrate. From the author’s rearing, the duration of larvae are: Male: 12-18 months; and Female: 12 months.
There is a breeding technique on this species. When larvae are singly reared, the female tend to emerge much earlier than the male. Although the imago of this species has a rather long life (8-12 months), it occasionally makes you difficult to mate them for the following generations. To avoid this, I suggest you to prepare for at least one large container where you would put both male and female larvae together until their emergence. By so doing, the female and male would emerge around the same time and it makes you easier to mate them. H. Kojima points out that the female larvae of this species might emit some sort of pheromone to prompt the male counterparts in the surroundings to undergo pupation in aggregation. This rearing method, however, would not promise you to bring out a growing potential of the male (or female) larva to the maximum. In another word, if you want to rear large male (or female) imagoes, they should be reared singly in a container of a large capacity. There may be exceptional cases, but that is the safest bet.
3.3 Larva sexing
For sexing, see the following picture, Figure 3.3
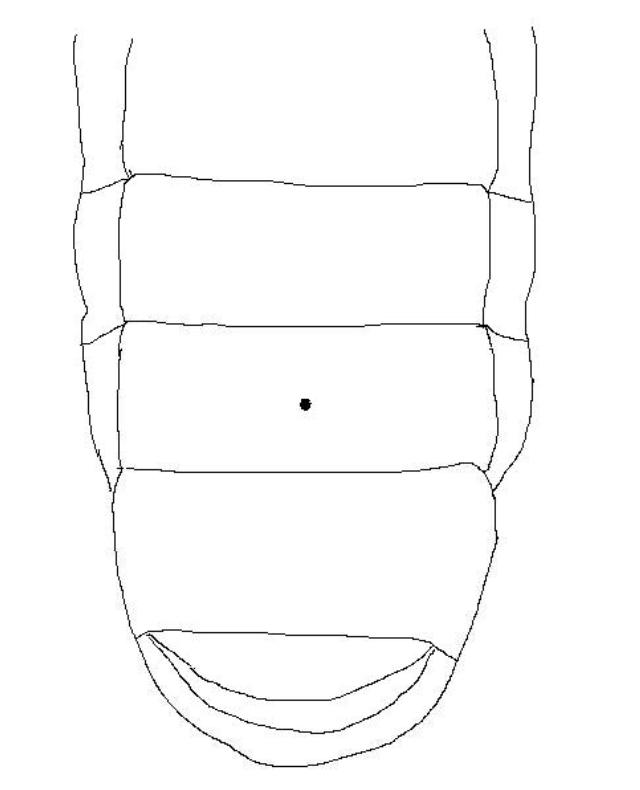
Figure 3.3 A tiny dent may be visible on the 9th abdominal segment of the ventral side of male larva after its mid-L2 stage. No dent on female larva. Besides, an L3 male often exceeds 100 grams in weight when it is fully grown. Whereas the female remains up to 80 grams.
3.4 Maintaining pupae
After larvae turn noticeably yellowish in colour, stop changing rearing substrates. Some time soon, the larvae make a pupal cell under the substrate and undergo pupation in it. The best advice I give you at this point is patience: wait until imagoes emerge from the substrate. It may take several months.
3.5 Breeding
Repeat the process: 3.1 Getting started.
4. A breeding/rearing substrate
If you live in a country where you can obtain natural food for the species you want to breed/rear, please skip this chapter. The natural food would be the best choice. If not, there are some substrates available for breeding and rearing rhinoceros beetles. On this page, I will choose one of these kinds. It is relatively easy-to-get and inexpensive. Its recipe is based on my direct hearing with H. Kojima, a Japan’s leading expert on Dynastine/Lucanid beetle breeding/rearing, and I have tested its performance by using it for breeding/rearing some rhinoceros beetles. So far, it has made an excellent performance in the beetles’ egg laying and larval growth. However, please notice that I will not take any responsibilities in event of any ill or arrested development or, in the worst case, death of your beetle larvae due to its use:
Bark compost (made of hardwood trees only, no coniferous trees): 90%
Poultry manure: 10%
Go to a garden center/shop nearest you and get them. Make sure that you should get the ones with no chemicals (the organic ones). After the two are mixed well, it is ready to serve. You can also use this substrate for breeding and rearing flower beetles and some stag beetles (e.g. Genus Odontolabis and Lucanus)
5. Acknowledgement
My special thanks are indebted to the following organizations and individuals: ‘The Beetle Ring’ (http://www.naturalworlds.org/beetlering/beetle_sites.htm) by Cameron Campbell, the administrator of ‘The Natural Worlds’ (http://www.naturalworlds.org/); ‘The Kanagawa Stag Beetle Club,’ a local chapter of Japan’s largest beetle hobbyist club, ‘The Stag Beetle Fools’ (http://www.mars.dti.ne.jp/~k-sugano/bakamono_web/index2e.html), and its members including Hiroshi Kojima; Benjamin Harink for sharing this wonderful hobby together and allowing me to contribute this article to his great beetle website; my father who has inspired me to pursue this interest; and my mother who has been patient enough for this unusual hobby of mine.
Contact:
I can be reached at http://www.geocities.com/kaytheguru/. Please feel free to visit my beetle website.
PS The following pictures are a male Hercules pupa and the imago, respectively. It was reared by the author to be 150 mm in length.
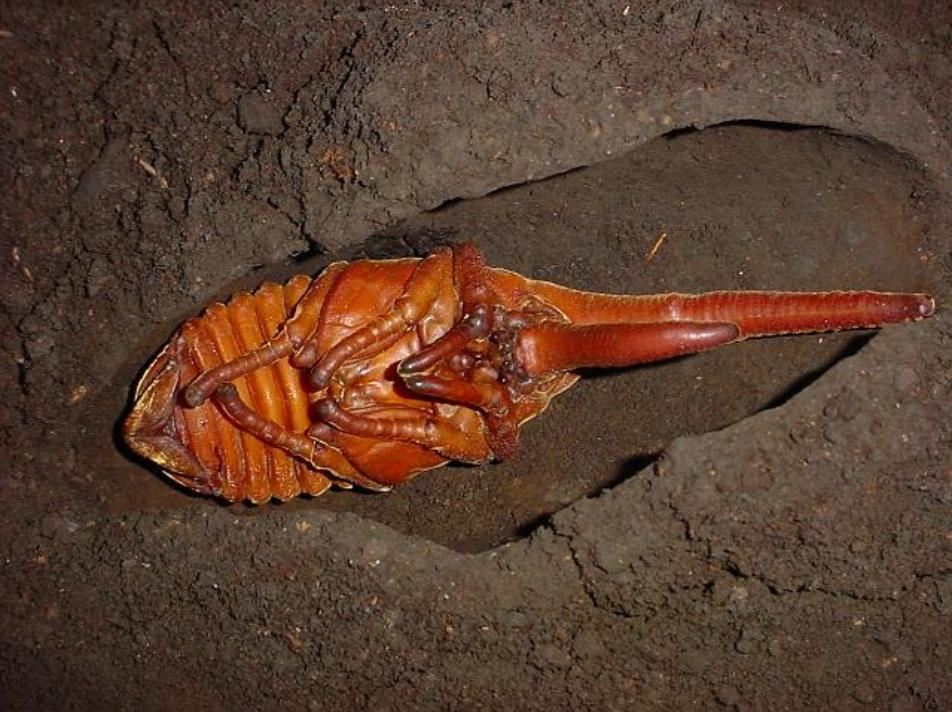

Figure 5.1 Shown in this picture is a male pupa of about 165 mm in length. Note that the maximum length of the pupal cell is about 190 mm. For the captive rearing of this individual, the author used a 60 liter container (see Figure 3.1.2), which was filled with hardened black dirt up to 10 cm high from the bottom and with rearing substrate (see 4. A breeding/rearing substrate) softly added on it for 20 cm high. The hardened bottom layer of black dirt helped the larva make this solid pupal cell.
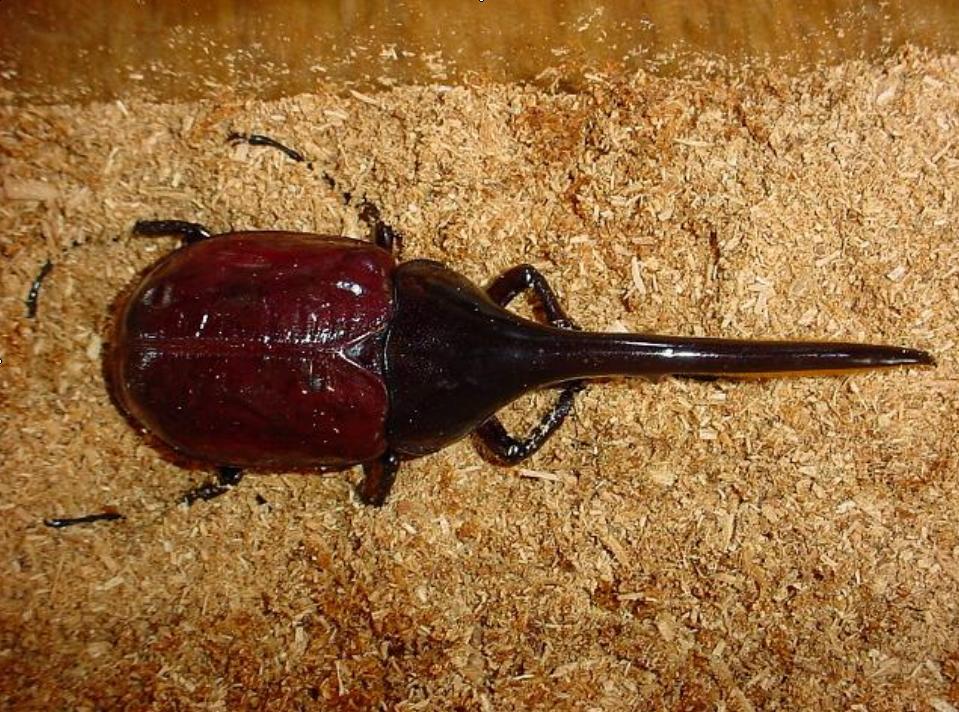

Figure 5.2 Shown in the picture is a 150 mm long male imago which emerged on March the 3rd in 2005 from the pupa shown in Figure 5.1. Captive reared by the author.



Hi, i’m stag beetle breeder in south korea.
i found this during search for some useful information of breeding beetles
and i think this is really, super good.
Can i share this report in my blog, with some translation?
this is really good information for me, and my friends.
Thank you~^^
Hi,
thanks on behalf of Kay. This is indeed a very good breeding report. I think you have to check with him if you can use this article for your blog.
I will send you an email with his contact details.
Good luck for your beetle rearing projects
Ben
Oh, i really appreciate to your response and your favor.
And i also agree with your opinion again. ( This is indeed a very good breeding report.)
Thank you ~^^
Hyun nam
Thank you and good luck with your beetle rearing. May I ask you, what Lucanidae are you breeding at the moment?
Warm regards
Benjamin
Now i breeding two species, Dorcus titanus castanicolor and Prosopocoilus inclinatus.
These are korean native species. Dorcus titanus castanicolor looks like Dorcus titanus palawanicus. If you look this, maybe you’ll think this is small size of palawanicus and Prosopocoilus inclinatus looks like Hexarthrius Mandibularis but not very simmilar.
They don’t have big size of body, so not popular in world.
But, i love my beetle.
Thank you!^^
Warm regards
Huyn nam
Hey,
I have been breeding P. inclinatus from Japan, and they are not so small. I do like them a lot. Same for Dorcus titanus castanicolor, it also is a beautiful species. Only thing I dislike in Dorcus is that they are always hsy and hidden, and that it is difficult to see them.
Anyhow, good luck with your breedings. Korea also has a nice Lucanus maculifemoratus dybowskii and mayn small species that are very interesting.
Warm regards
Benjamin
Oh, it’s like me, i also dislike species those are always hidden.
And i agree with your words, little beetles are very interesting because of their
brisk character. They always move.
And i also wonder that whit kinds of beetles you rearing.
May I ask you, what beetles (Include rhinoceros) are you breeding at the moment?
I always thank you for your kind response.
Thank you!
Warm regards
Hyun nam
Since I just moved to a new country, I do not have any beetles at the moment.
Just a few weeks back, I was keeping and rearing Megasoma anubis, Dorcus brevis, Dorcus curivdens binodulosus ‘red eyes’, Prosopocoilus hasterti moinieri, Mesotopus tarandus, Taeniodera egregia, Lamprima adolphinae and some more.
I do miss beetle breeding already, and hope that I can start soon again.
Warm regards
Benjamin
Oh, I hope that you can start soon again rearing.
You reating various and attractive species. I just envy to you.
Dorcus curivdens binodulosus ‘red eyes’ is also korean native species
and i will rearing that kind of specie soon.
Thank you!
Warm regards
Hyun nam
Hi,
yes, these are nice. Unfortunately, I cannot raise and keep any exotic species over here. So, I will concentrate on US local species for some time now.
Dorcus curvidens is easy to breed and quite beautiful. I only do not like that they are very shy, and you never really see them in the breeding box. The good thing though, is that they live for a very long time.
Good luck with getting this species.
By the way, do you know of a list or source of Korean beetles? I only know very few species from Korea, but there must be more.
Warm regards
Ben